INUNCAMis the plan of the Community of Madrid to act in front of rains and floods such as those expected, for example, by Aemet for this Thursday by the Borrasca Martinho. This plan includes a detailed map of the areas of the Province prone to floods, which indicates that Only 2% of the territory from the Community of Madrid, equivalent to about 1,836 hectares, it is classified as high -risk flood area.
Within this reduced percentage, places such as Aranjuezthe Madrid City and certain areas of the regional southwest. In these sites, as well as in others, three flood risk categories are identified, considered both in the regional plan and in local procedures: the derivative of the breakdown of dams or other hydraulic infrastructure, the floods caused by heavy rains and those originated by overflows of rivers or channels.
The #AgenteForestascm They travel roads, tracks and roads to ensure that they are passable and monitor floods in the river flow.
Respect the beacon zones and avoid proximities to water courses or flooded areas.#Inuncam#ASEM112 pic.twitter.com/3qSSW90FMT
– 112 Community of Madrid (@112cmadrid) March 20, 2025
In Madrid capital, flood areas that affect homes are in the Barajas district. And there are public endowments that can be affected by floods, such as Aravaca schools Located in La Vega del Arroyo de Pozuelo and the sports facilities built Next to the Manzanares banksbefore the channeling as it passes through the urban nucleus of Madrid.
Within this group are spaces of the Campo Villa de Madrid, he Puerta de Hierro Sports Park or part of the municipal nurseries.
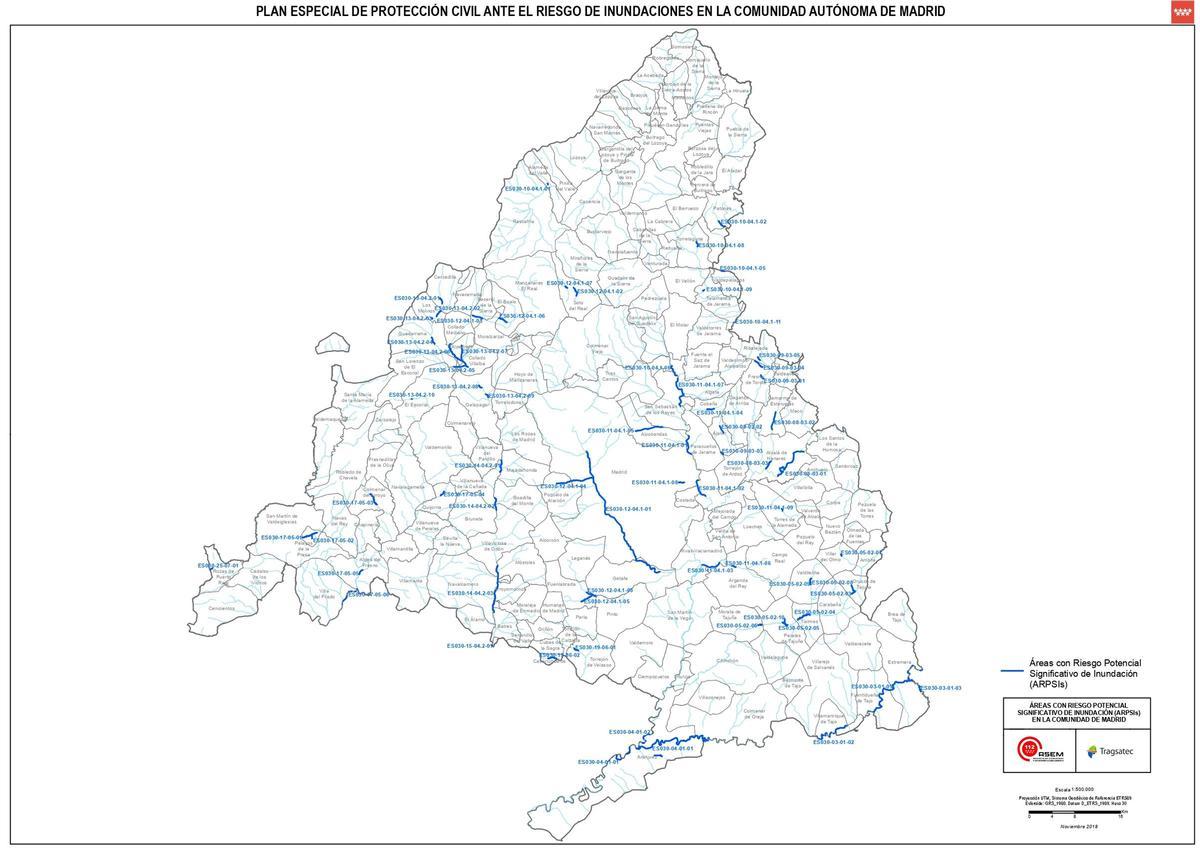
 Map of areas with a flood risk of the Community of Madrid. / ASEM112 Community of Madrid
Map of areas with a flood risk of the Community of Madrid. / ASEM112 Community of MadridThe flood areas of the Community of Madrid have gained special relevance in recent days due to the heavy rains that have affected the region, leaving the swamps to the limit of their capacity. These copious rainfall have generated concern in the most vulnerable areas.
Among the most exposed areas are Aranjuez, Madrid Capital and several locations in the southwest of the region. These areas face three main types of risks:
- Dam rupture or other hydraulic infrastructure
- the floods For intense rainfall
- the overflows of rivers or channels.
With the swamps full, such as those of the Tajo Basin or the Lozoya, the controlled unpacking has become an inevitable measure to avoid major damage. After the latest rains, reservoirs such as The Atazar or that of Santillana They have reached critical levels, forcing the authorities to release water gradually. Although these operations seek to prevent disasters, they are not exempt from consequences for the areas Downstreamespecially in riverside municipalities.
In Aranjuez, for example, the Confluence of the Tajo rivers and Jarama It has historically been a critical point. The recent floods and the released water from the reservoirs have raised the alert level among the neighbors.
In Madrid capital, areas CERCANAS TO THE MANZANARES RIVERalthough regulated by dams such as El Pardo, they have also experienced Airgrations in extreme rain episodes. For its part, the southwest of the region, with municipalities such as Navalcarnero either Villamantasuffers the consequences of less controlled channels that easily overflow in the face of excess water.
The management of the full swamps raises a dilemma: maintaining stored water increases the risk of uncontrolled breakage or overflow, while the unreasonable can aggravate floods in the low areas. The authorities have intensified the coordination between the Hydrographic Confederation of the Tagus, the municipalities and the emergency services to mitigate the effects. In addition, the INUNCAM provides preventive measures such as CAUZ CLEANING, INFRASTRUCTURES REINFORCEMENT AND EARLY COMMUNICATION TO THE POPULATION.






